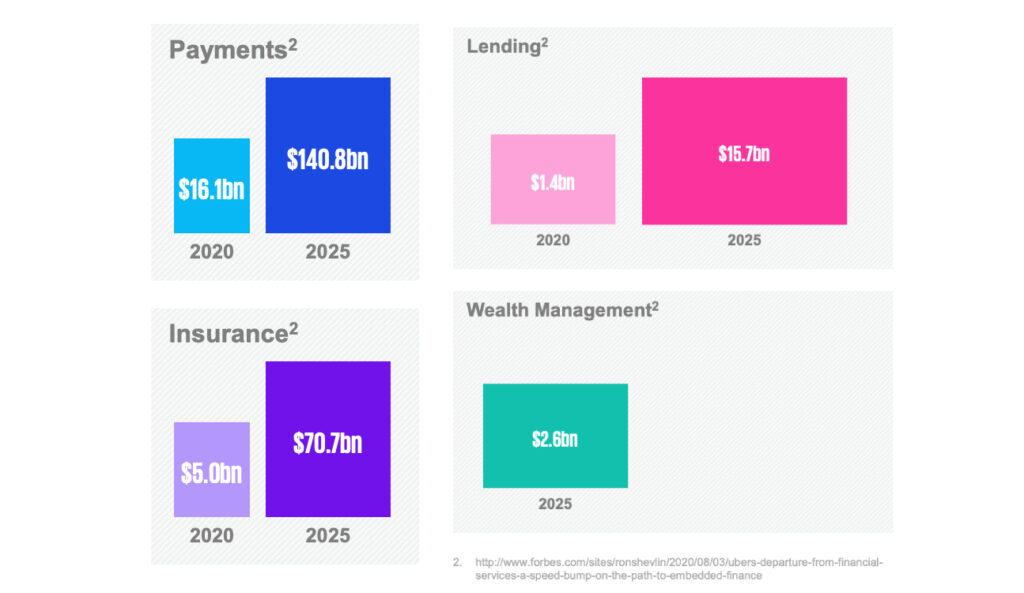
The use of cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI) has enabled fintechs to offer innovative and disruptive business models that have the potential to shake up the traditional financial industry. This, combined with the growing adoption of BaaS solutions, has led to the growth of the embedded finance industry, which is expected – according to KPMG – to reach $230 billion by 2025.
The embedded finance industry has seen significant growth in the past few years, with the integration of payment capabilities into many platform businesses.
While the concept of embedded finance is not new, having originated from traditional point of sale transactions, it has contributed to the rapid increase in online transactions and credit.
In the Asia Pacific region, the embedded finance industry is expected to reach $110 billion in 2022 and is estimated to continue growing, reaching $360 billion by 2029 with a compound annual growth rate of 24.4%.
This growth is likely to be driven by changing demographics, consumer buying behavior influenced by financial literacy, financial inclusion, and the proliferation of online transactions. Ultimately, embedded finance is expected to benefit both customers and businesses, potentially even expanding into business-to-business transactions to facilitate trade and improve supply chain efficiency. Investors are expected to play a crucial role in funding embedded finance, leading to a strong flow of deals into embedded finance and decentralized finance (DeFi) supporting business models and platforms.
In the Asia Pacific region, the embedded finance industry is expected to reach $110 billion in 2022 and is estimated to continue growing, reaching $360 billion by 2029 with a compound annual growth rate of 24.4%
- KPMG -
The benefit of Embedded finance implementation
The banking and financial services sector is constantly undergoing change, with traditional financial products and services being disrupted by a range of factors, including innovative technologies like cloud computing and artificial intelligence, emerging fintechs with innovative business models, and the use of application programming interfaces (APIs) to support Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS).
One of the ways in which this disruption is occurring is through the concept of embedded finance, in which non-financial companies offer financial services to their customers at the point of need. A common example of this is a company allowing customers to make purchases through their website or app using various payment options, such as credit cards, digital wallets, or installment financing. This embeds finance into the transaction process and streamlines the customer experience.
Many non-financial companies offer embedded finance solutions through partnerships with fintech companies. These arrangements can be mutually beneficial and have become a popular business model. Adoption of embedded finance has been on the rise in recent years, and it is expected to continue growing exponentially in the coming years.
4 main categories of embedded finance
There are four main categories of embedded finance:- Embedded payments: This refers to the integration of digital payment options within the platforms or apps of non-financial companies. This enhances customer convenience by allowing them to pay for goods or services without having to leave the company’s website or app. Examples include digital wallets and instant payment options.
- Embedded insurance: This involves the real-time bundling and sale of insurance products as part of the sale of a separate product or service. This allows consumers to buy insurance products related to or tangentially connected to the item they are purchasing at the point of sale. Examples include the offering of add-on insurance when purchasing electronics online or embedded insurance in ride-hailing services.
- Embedded lending: This refers to the integration of lending services within the digital platforms of non-financial companies. Examples include “buy now, pay later” options, financing for small and medium-sized enterprises, and co-branded credit cards. The “buy now, pay later” model, in particular, has seen significant growth in recent years and allows customers to make purchases immediately while deferring payment to a later date.
- Embedded investing/wealth management: This refers to the inclusion of investment products within the digital platforms of non-financial companies. Examples include health insurance providers offering investment options to customers through their existing accounts or e-commerce and ride-hailing companies allowing customers to purchase cryptocurrencies using the available balance in their linked digital wallets. While interest in embedded payments, lending, and insurance has grown significantly in recent years, the embedded investing and wealth management space is still in its early stages. However, service providers are starting to integrate wealth and investment services within their core product offerings.
Our research on embedded finance brings us to believe
that Embeeded Finance will increasingly feature as an important driver of online
transactions and support customer engagement and speed of
transacting.
- KPMG -
Value chain of embedded finance
When it comes to the value chain of embedded finance, there are three main categories of players: providers of financial services, infrastructure providers, and platforms and marketplaces. Historically, each of these types of businesses has had a distinct role from the others. However, as technology becomes more sophisticated and market players compete to capture a larger share of revenue by expanding across the value chain, the lines between these categories are blurring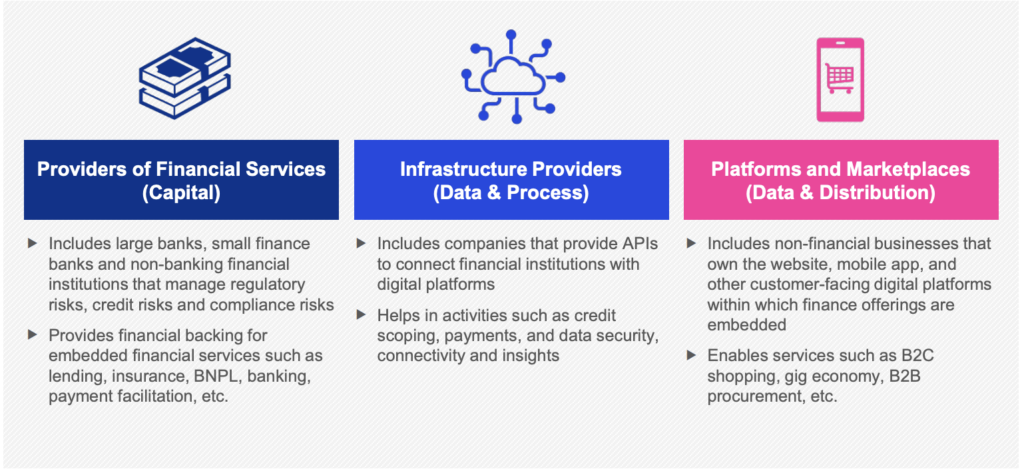
Source: KPMG
Focus on sector applications
The success and wide adoption of embedded finance in the retail and e-commerce space is driving companies to consider use cases for other sectors. While the use of embedded finance within different sectors might follow different adoption and maturity curves, the opportunities associated with the use of embedded finance are vast—making a future where financial services are highly embedded across sectors almost inevitable.
In the KMPG research, there is a deepening in the various sectors where Embedded Finance can have a high value impact, we suggest to read.
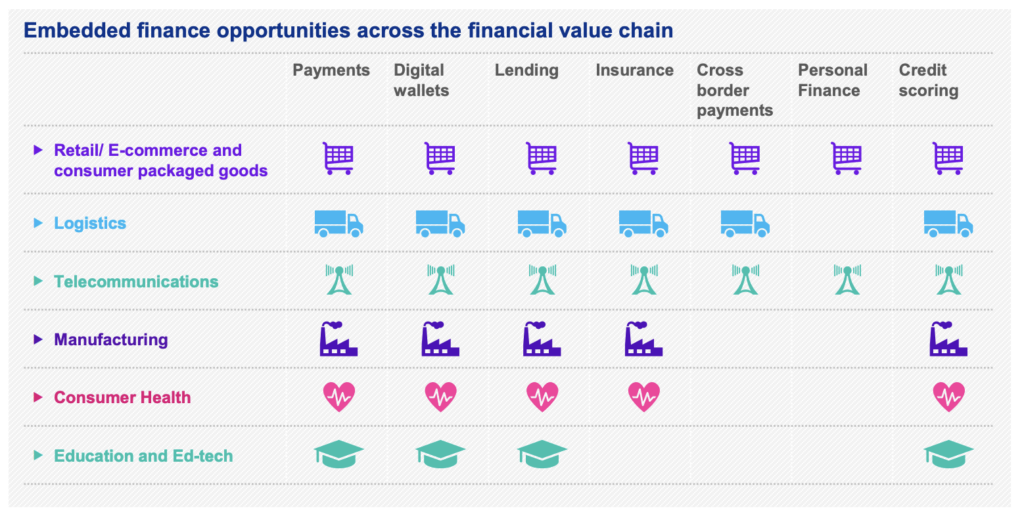
Source: KPMG

